Transmissibility Curves for Vibration Isolation
Tables, Platforms, Isolators & Systems
Performance:
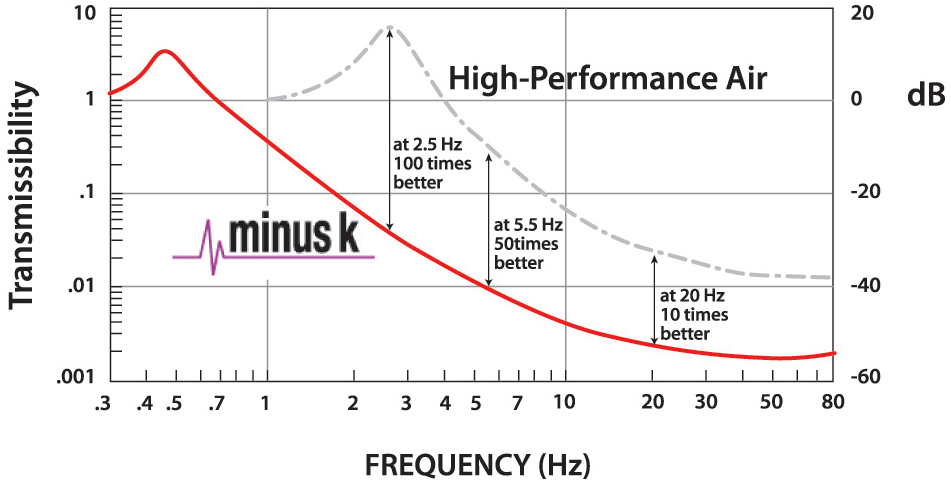
Based on field testing and user evaluations, the Minus
K 1/2-Hz vibration isolation platforms and workstations
perform about 10 to 100 times better than high-performance
air tables depending on the vibration isolation frequencies.
They also perform better than active or electronic-cancellation
systems.
The transmissibility curves, which compare top-performing
air tables with the typical Minus K 1/2-Hz performance,
are shown below. Minus K isolators (adjusted to 1/2 Hz)
achieve 93% isolation efficiency at 2 Hz, 99% at 5 Hz, and
99.7% at 10 Hz. Isolation performance closely follows that
of an ideal undamped single DOF system up to about 10 Hz
and reaches a floor in the transmissibility curve with some
resonances at the higher frequencies.
The Minus K curve below is typical for any Minus K 1/2-Hz
system, horizontal or vertical. Measured transmissibility
curves for some Minus K bench top products are also shown
below:
Transmissibility test procedure:
The transmissibility curves provided by Minus K Technology
are generated using a Stanford Research Instruments SR785
Dynamic Signal Analyzer. The output source of the SR785
is set to generate a swept sine signal. This signal is fed
into a Labworks PA-138 power amplifier. The amplifier drives
a Labworks ET-126 electrodynamic shaker. The shaker is mounted
in a heavily reinforced frame that also supports a 650BM-1
isolator. This support isolator has been adjusted to about
2.75 Hz. It has also been modified to work only in the vertical
direction. This isolator supports a heavy top plate and
whatever ballast weight is needed to bring the total payload
including the test isolator up to around 650 pounds.
Transmissibility as it applies to our isolators is a ratio
of the output signal on the top plate divided by the input
signal that the base of the isolator sees. One can also
think of it as the ratio of what gets through the isolator
divided by what is present on the isolator support. Two
similar accelerometers are used to acquire the input and
output signals. The input accelerometer is attached to the
heavy top plate on the 650BM-1 support isolator. The test
isolator rests on the heavy top plate as well. This way
the accelerometer measures the vibrations that are fed to
the isolator. The output accelerometer is placed on top
of the properly loaded test isolator top plate. Both accelerometers
are held in place with a thin layer of seismic wax. This
works quite well, providing a secure, yet easy to undo bond
for measurement.
The SR785 acquires both sets of data, calculates their ratio
and displays the ratio as transmissibility..
The horizontal transmissibility was acquired in much the
same way. The differences were that the support isolator
was allowed to move horizontally. The electrodynamic
shaker was mounted horizontally. The accelerometers
were mounted on their sides, which allowed the ratio of
horizontal data to be calculated and displayed as horizontal
transmissibility.
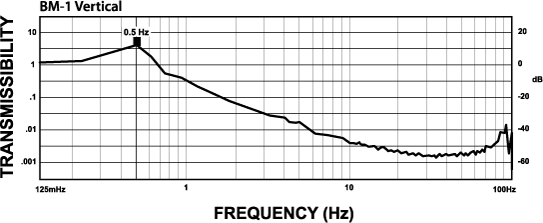
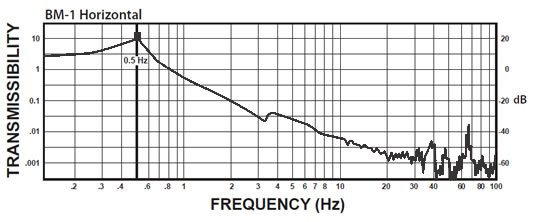
BM-1 Isolator:
The curve below shows the typical vertical 1/2 Hz performance of the BM-1. It offers 10-100 times better performance than typical high-performance air tables.
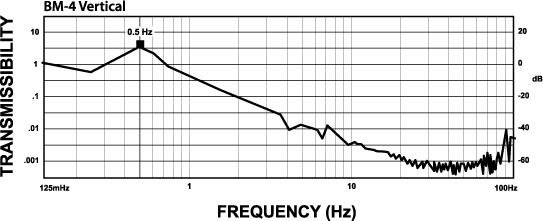
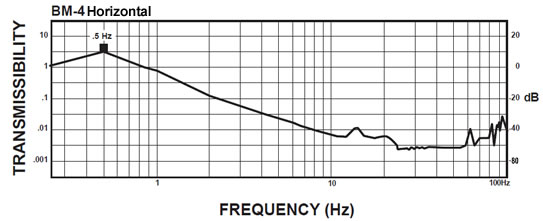
BM-4 Isolator:
The curve below shows the typical vertical 1/2 Hz performance of the BM-4. It offers 10-100 times better performance than typical high-performance air tables.
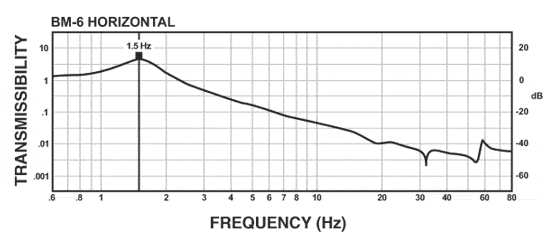
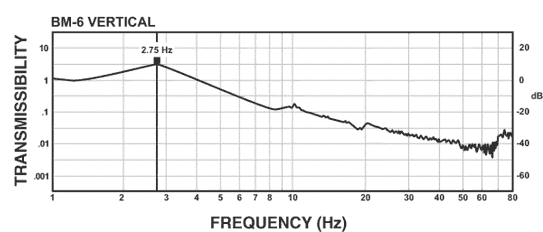
BM-6 Isolator:
The curves below demonstrate the better-than-air performance that the BM-6 delivers. Vertically, the BM-6 offers a resonant frequency that is comparable to or better than most air tables. Horizontally, the BM-6 offers much better performance than typical air tables, which can have horizontal frequencies as high as 4-5 Hz.
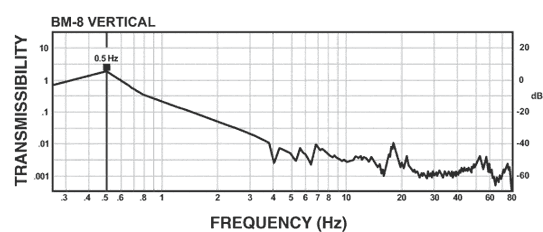
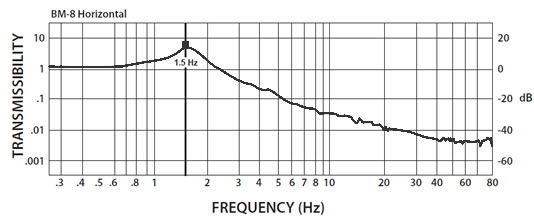
BM-8 Isolator:
The curve below demonstrates the vertical 1/2 Hz performance of the BM-8. The BM-8 delivers the high performance of our larger isolators in a package only 4.6 inches tall. The horizontal performance of the BM-8 is the same as that of the BM-6.
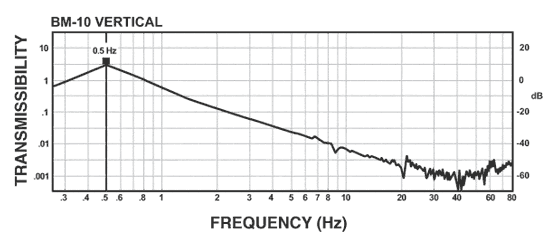
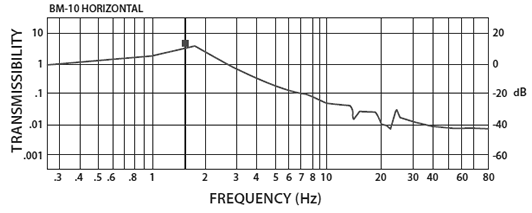
BM-10 Isolator:
The curve below shows the vertical 1/2 Hz performance of the BM-10. It offers 10-100 times better performance than an air table in a package many times smaller. The horizontal isolation performance of the BM-10 is the same as that of the BM-6.
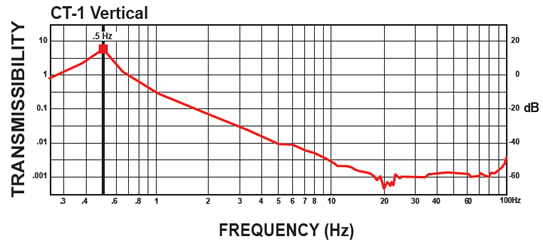
CT-1 Isolator:
The curves below shows the 1/2 Hz performance of the CT-1. It offers 10-100 times better performance than an air table.
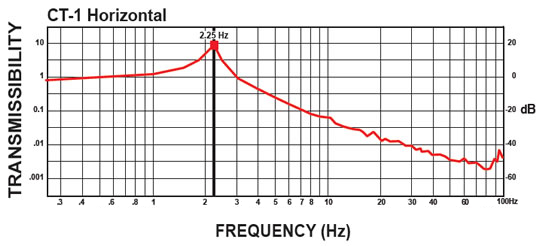
CT-2 Isolator:
The curves below shows the 1/2 Hz performance of the CT-2. It offers 10-100 times better performance than an air table.
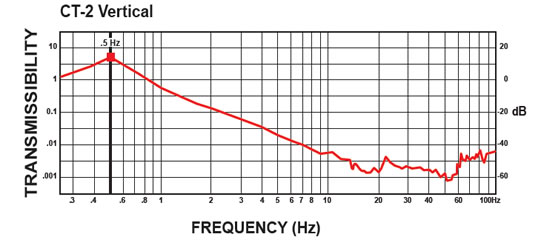
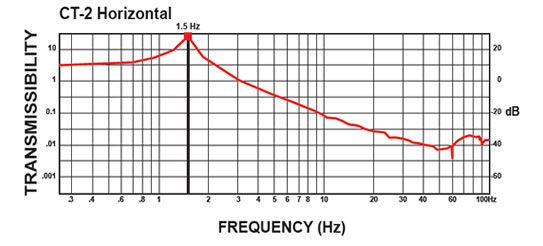
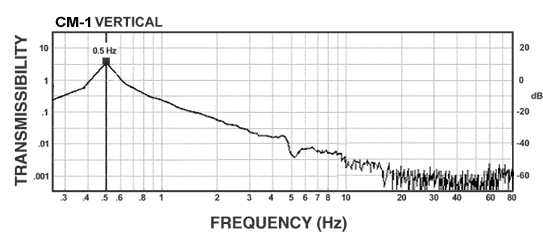
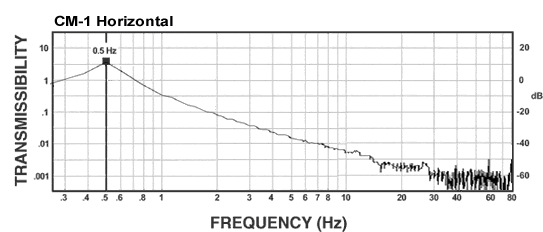
CM-1 Isolator:
The curves below shows the 1/2 Hz performance of the CM-1. It offers 10-100 times better performance than an air table.
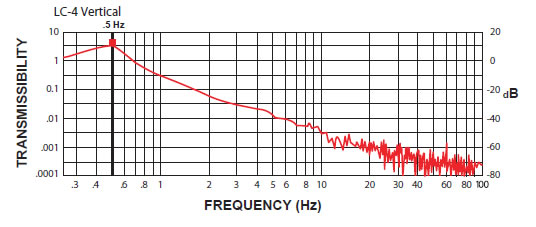
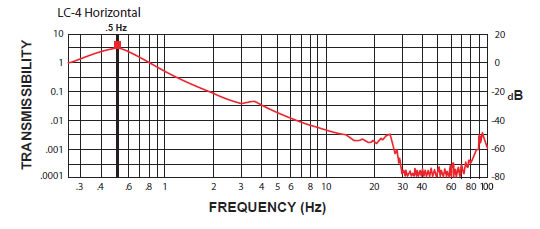
LC-4 Isolator:
The curves below shows the 1/2 Hz performance of the LC-4. It offers 10-100 times better performance than an air table.
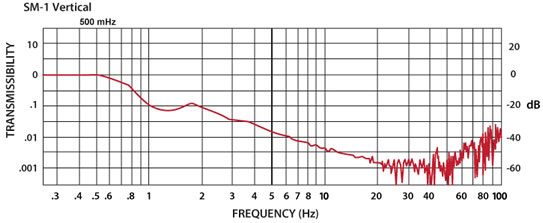
SM-1 Isolator:
The curve below shows the 1/2 Hz performance
of the SM-1.
(The curve below about 2 Hz is not valid. The curve was measured from ambient vibrations and they were too low to get valid results below about 2 Hz. The actual curve should be quite similar to those of our other 0.5 Hz isolators.)
The ambient horizontal vibrations at our facility are too low to measure a valid horizontal transmissibility curve. We expect the actual curve is quite similar to those of our other 0.5 Hz isolators.